The deformation of the arthrosis of the knee joint is a polyetiological disease. This means that there are many reasons for its development. In some cases, gonarthrosis is called secondary if the most dominant cause can be assigned. In this case, if a clear cause is not determined, the diagnosis of primary or idiopathic osteoarthritis of the knee joint is determined.

- Deforming osteoarthritis of the medial part of the femoral joint;
- Deforming osteoarthritis of the lateral part of the femoral joint;
- Deformation of the osteoarthritis of the femoral member joint.
Usually the destruction of the common cartilage occurs in the process of physiological covering the entire organism, ie during aging. The pathological destruction of the cartilage is taken into account when it occurs before the time or more intensive speed. The average age in which the first signs of cartilage regeneration can manifest on a completely legitimate basis is 40 to 50 years. With deforming osteoarthritis, the disease debut in childhood with the first manifestations of 16 to 18 years and in some cases even earlier. However, this is not a reason for despair.
The mechanism of the development of the disease is a vicious circle in which the final connections start the initial and so on to infinity. However, each round of this circle tightens the condition of the cartilage and leads to the progress of the disease and thus in the chain. With primary gonarthrosis, the reason why a vicious circle comes onto the market is unknown. Nevertheless, his subsequent connections are carefully examined in order to influence them and slow down the progression of the disease.
The deformation of osteoarthritis arises approximately as follows. The daily joint cartilage of the knee joint experiences thousands of shocks that you have to dismantle so as not to damage the tender structures of the human body such as internal organs and brain. Over time, due to the data of conceals of the brain, microscopic cracks are formed in the cloudy layer, which are filled with synovial fluid even after a certain period of time and turn into microdists. Neighboring microdists tend to combine and form larger cysts.
The size of the cysts of the corneaum is gradually increasing to press the blood capillaries that feed the cartilage tissue from the side of the bone. The supply of oxygen and substances that are necessary to maintain the important activity worsens, which leads to a slower synthesis of the type -2 collages.
The transport of cartilage leads to two negative consequences. First, this leads to a deterioration in the depreciation properties and a more intensive formation of new microreters in the sub -layer. Secondly, due to the compression of the cartilage, his density increases, which adversely influences the second mechanism of his diet on the diffusion of synovial fluid in the thickness of the cartilage tissue.
The destruction of the articular cartilage does not remain unnoticed on the scale of the entire organism. As a compensatory reaction in the focus of the washing of cartilage, the activity of chondroblasts - young cells that synthesize new cartilage tissue takes. However, this compensation mechanism is imperfect, and its imperfection lies in the fact that the majority of the cartilage tissue is not formed at the scene of the greatest destruction of the cartilage, but has no stress on the cartilage.
As a result, the cone -shaped cartilage growth on the edges of the joint chondroophyte are formed. These chondroophytes do not manifest themselves clinically when the ossification processes begin in them. Okreten, chondroophytes harden and transform into common people as spikes. As a rule, the appearance of spikes is always accompanied by the occurrence of pain and the development of inflammation in the joint. This is due to the fact that osteophytes touch the cartilage tissue and the synovial bowl during the movement of the joint, which makes it mechanically harmful.
As a result, every complication of the disposal arthrosis leads to acceleration of the progress of pathological changes in the cartilage. However, if you know the mechanism of developing gonar rose, you can successfully influence some of your connections to slow down your electricity and to improve a long -term forecast.
Secondary gonarthrosis differs from the primary, since the main reason is known that brought a vicious circle of destruction of the common cartilage onto the market. The further course of the disease takes place in the same way as in primary gonarthrosis, with the peculiarity that the disease is constantly tightened by the effects of negative factors associated with the underlying disease. For this reason, the course of the secondary osteoarthritis of the knee joint is generally more aggressive.
- Injuries (acute and chronic);
- Congenital varus or valgus deformation of the lower extremities;
- Congenital shortening one of the lower extremities;
- Hypermobility syndrome of the knee joint;
- Congenital dysplasia of the knee joint;
- Chondrocalcinosis;
- Osteomyelitis;
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Acromegaly;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Obesity;
- Hypothyroidism;
- Fraud etc.
Post -traumatic deformation arthrosis is divided into acute and chronic. The acute form of the disease develops more often after a serious injury -
, the appearance or partly on the side of the bone. The chronic form of the disease develops longer and is usually associated with frequent and slight injuries to the joint. Such conditions are created by builders, street workers, moving companies, etc.
In acute gonarthrosis, the mechanism of the disease is associated with severe inflammatory changes in the joint cavity, namely with lymphostasis, increased pressure in the joint cavity and a change in the composition of the synovial fluid. Excessive acceleration of the growth of the new cartilage tissue leads to a deformation of the joint surface at the fracture position and the growth of osteophytes.
In chronic gonar rose, no severe inflammatory process is observed, but the frequent and intensive stress on the cartilage tissue leads to its quick compression, the formation of microresses and the deterioration in cartilage supply with nutrients both from the side of the bone and the joint gap.
People with this pathology can be found quite often. Its essence is to change the shape of the legs. In the event of varior, the legs are curved outwards in a horizontal level. In other words, between the patient's legs, the room is more than in healthy people. With Valgus deformation, the legs have an X-shaped shape when the knees are in contact with each other. Due to fractures of the lower extremities, both pathologies can both genetically programmed and develop themselves during the lifespan.
In both cases, the load increases on one of the sides of the knee joint with Varus deformation on the side pages and with valgus deformation on the media pages. Due to the fact that the patient's same weight presses on a smaller area, an early laundry of the cartilage occurs, accompanied by inflammation, pain and morning rigidity.
The innate shortening of one of the legs is a result of anomalies or can develop a few years after birth as a result of the birth injury. As in the previous case, an uneven weight distribution occurs and the normal leg takes on a large load. As a result, the joint cartilage of the knee joint of a healthy leg is subject to structural changes that lead to a deformation of osteoarthritis.
This pathological state is not a disease, but can certainly lead to it. This syndrome means an excessive mobility of the ligamentous and consistent apparatus in which the joint movement of the joints within normal axes can increase significantly. Such patients almost never suspect that they have such a feature because they live with this life all their lives and believe that other people work in the same way.
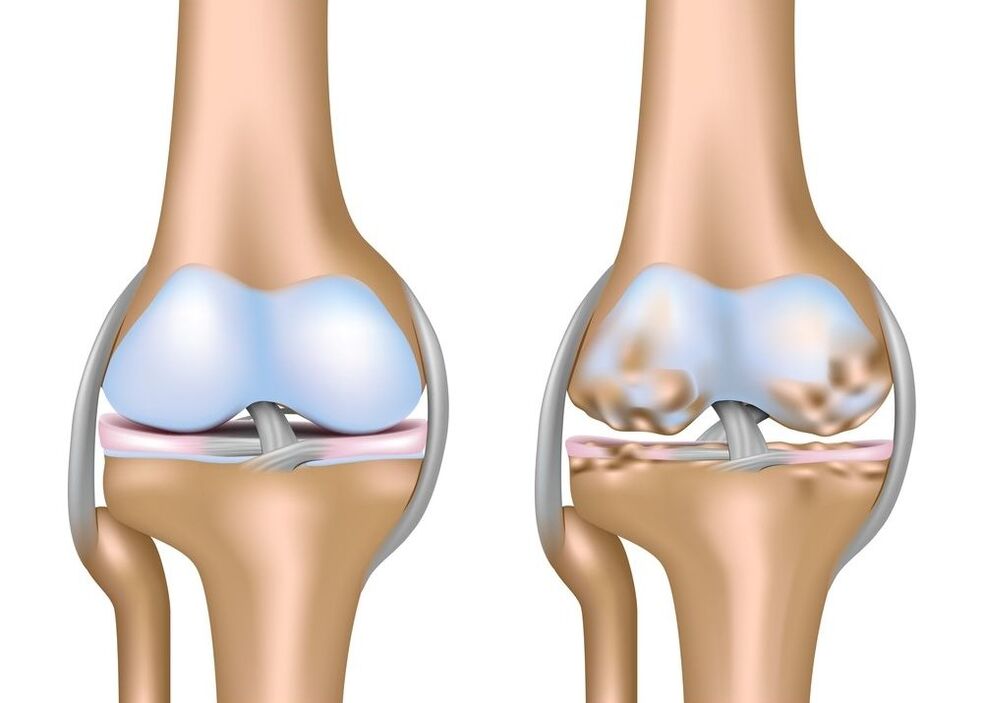
A sign of hypermores of the knee joint is the formation of a stupid angle between the front surfaces of the thigh and the lower leg with maximum leg. In other words, the knees bend as they were and their legs have a passionate form. In addition, such patients can easily reach the forearm with their thumb, reach their heads to the legs and in principle have congenital flexibility.
Symptoms of the arthrosis of the knee joint
In the initial development phase, the pathology manifests itself through pain in the knee, moderately expressed and arises in the movement when it moves along the steps.
An unpleasant symptom can occur if a person spends a lot of time to stand or climb after they are in a seating position for a long time.
Health usually improves in peace.
Sharp intensive severe pain occurs spontaneously.
Most patients previously had longer symptoms during physical activity and when walking. In this case, growing pain can be the main sign for the development of gonarthrosis.
The disease gradually develops for several months or years if it has no visible deformation and severe pain. During this time, however, uncomfortable in the knees that occur from time to time.
Remember, the earlier you consult a doctor, the easier and more successfully the treatment is passed.
Do not delay a visit to a specialist and wait for irreversible episodes. Take measures as soon as you notice the symptoms of the disease.
The obvious signs of osteoarthritis of the knee joint manifest themselves as the structure of the cartilage shells, a decrease in the production of synovial fluid and damage to the joint bag. In the initial phase of increasing the pathological changes, there are usually no pronounced symptoms, but at the same time there may be slight rigidity in the morning.
If you are pronounced and various symptoms occur, arthrosis is usually already in the late stage of your development. At this point there is already serious damage to the structures of the knee joint, so that the disease goes into the acute phase. The characteristic manifestations of the acute development period of arthrosis include:
- Increased pain;
- Gear change;
- Lameness;
- Crunch when moving;
- Swelling of soft tissues;
- an increase in the knee due to the accumulation of liquid in it;
- Limitation of mobility in the joint.
If the knee arthrosis develops, the symptoms can grow long enough. However, if the disease merges into the last three manifestation of a disturbance of the joint, the quality of life significantly reduces the quality of life.
- The synovial shell against the background of the damage to the articular surfaces begins to ignite, which leads to a violation of the mobility of the entire joint.
- Every movement with a damaged joint can be very painful.
- In the case of palpation, a significant increase in the local body temperature is determined.
- As a rule, the effective treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint with conservative methods is only possible in the early stage of the development of the disease.
- If signs of the disease appear, contact a doctor for consultation.
When developing such a disease such as the arthrosis of the knee, the symptoms and treatment are connected, since in the early stages of the development of the disease, the joint surfaces can still be completely restored and improved by local metabolism. In the later stages of drug treatment of osteoarthritis, the knee joints in the later stadiums cannot look positive.
The osteoarthritis of the 1st degree is almost without visible symptoms. This development phase is characterized by:
- Fatigue in the legs;
- A slight decrease in mobility, which is usually observed immediately after sleep.
Pain symptoms, if and occur, manifest themselves to a small extent. At this moment, the arthrosis of the knee in the X rays in the form of small bumps on the cartilage tissue and the surface of the bones looks like.
With osteoarthritis of the 2nd degree knee joint, the symptoms are more pronounced. Pain already arises from the minimum load or immediately afterwards. In the affected part of the leg, the pain is caused by almost every movement. After a pretty long break, it usually goes off completely. However, the next physical acts immediately cause pain.
In roughly the second stage of the development of the disease, the pain sensations are added:
- Crunch in the knee joint during the movements;
- a reduced opportunity to bastard the leg normally in the knee;
- Change of bones together;
- Progressive synovitis.
A rough arthrosis crisis of joints is usually hardly audible at first, but with the course of the disease it becomes very loud and different. When trying to bend your leg in your knee, a sharp pain occurs. In some cases, this is only possible up to a corner of 90 degrees and then with difficulty and overcoming pain. The change in the shape of the joint is also obvious, which is also exacerbated by the accumulation of pathological fluid.
The characteristic features of the 3rd arthrosis degree are severe pain that are independent of the amount, the intensity of physical activity. The joint also disturbs a person at night, which leads to considerable inconvenience.
The X-ray image can show global changes in cartilage, joint surface, non-characteristic growth. O-shaped or x-shaped curvature leads to a person to a disability. These are the consequences that the cartilage tissue has already worn out and the bone tissue went into the "movement".
Gonarthrosis is a disease of degenerative-dystrophic nature in which the destruction of cartilage occurs and the joint is deformed. Signs of the disease are severe pain, deformation of the limbs, an uneven distribution of the load on the bone muscular system, the development of complications and a significant decrease in mobility to the disability of the patient.





















